China's Robot Revolution: Tackling Quality and Labor Shortages
 Kirti Rathod
Kirti Rathod- 18 Mar 2024
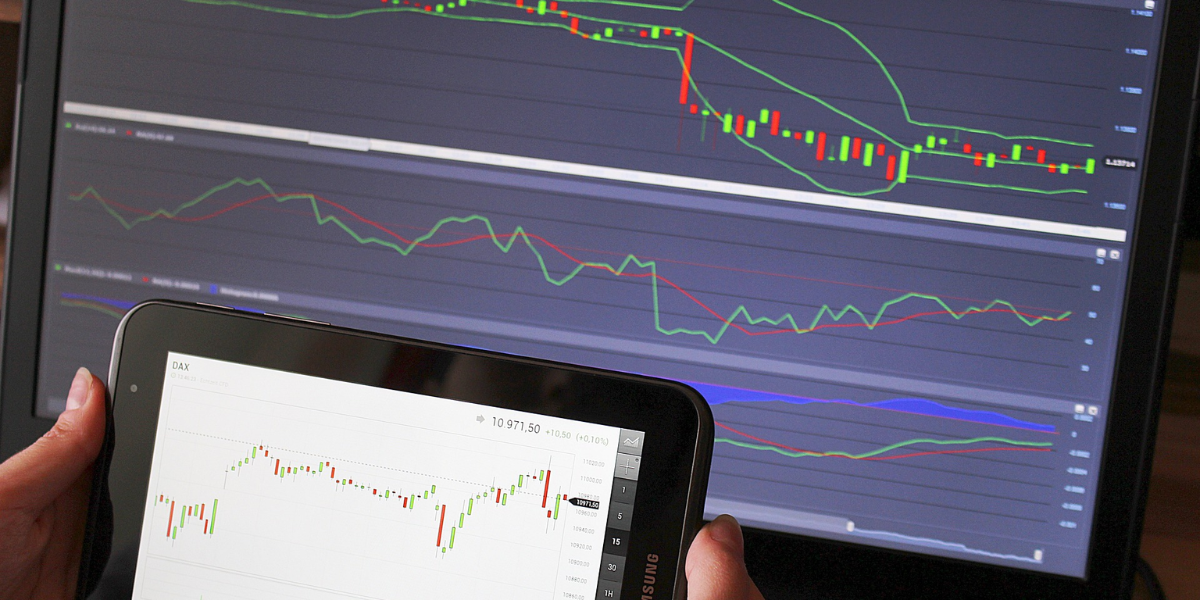
At the 2023 World Robot Conference, it was shown that China's use of robots in manufacturing has significantly increased, with "robot density" going up to 392 from just 68 in 2016. This increase indicates that robots are taking over many jobs previously done by people. China is using robots to address challenges like its aging population, to boost the quality of its products, to grow its exports, and to deal with trade pressures from the US.
In Dongguan, a city known for its intense industrial activity in southern China, the traditional manufacturing environment is undergoing a significant change. The once common sight of noisy factories filled with rows of workers, immersed in the smell of smoke and sweat, is becoming rare.
Today, the manufacturing floors that used to employ hundreds of thousands of workers have been replaced by industrial robots. These robots, capable of performing multiple functions, have taken over the tasks of several factory departments. As a result, only a small team of mechanics and engineers is needed to manage these automated systems.
A long time ago, factories started using robots because it helped them save money by not spending as much on paying workers. Banks were happy to lend money to buy these high-tech robots because it meant businesses didn't need to use their own money all at once.
Demographic Challenges and Government Response
Meanwhile, the government changed the rules that used to limit families to only one child, hoping people would start having more kids. But, they discovered that young couples didn't really want a second child, and many women didn't want to have children at all. In India, the situation is different because there are many young people.
Addressing Labor Shortages with Technology
In China, the number of people who are at the right age to work, meaning those between 16 and 59, is decreasing. There were 875.6 million people in this age group in 2022, down from 896.4 million in 2019. At the same time, the number of people older than 65 went up to 209.78 million from 176 million in 2019.
This drop in the working-age population, partly due to the one-child policy, is causing a shortage of workers in industries. China is getting older, and soon there won't be enough people to work. The country is looking at using humanoid robots as a solution. The government's technology ministry has made a plan to start mass-producing these robots by 2025. They want to create new technologies and make sure there are enough important parts for these robots to help with the worker shortage.
Expanding Robot Use Across Sectors
By 2027, humanoid robots are expected to become a key driver of economic growth in China. The country plans to significantly enhance robot technology, establish a secure and dependable supply chain for robot manufacturing, build an industry that can compete globally, and achieve a level of overall capability that matches the best in the world.
In 2021, China surpassed the United States to rank as the fifth most robot-intensive country globally, as per the World Robotics 2022 report.
The government has urged sectors like healthcare, domestic services, farming, and logistics to increase their use of humanoid robots. These robots are seen as the next big technological breakthrough, similar to the impact of computers, smartphones, and electric vehicles. They are expected to drastically alter both the production processes and daily life, potentially changing the global industrial landscape.